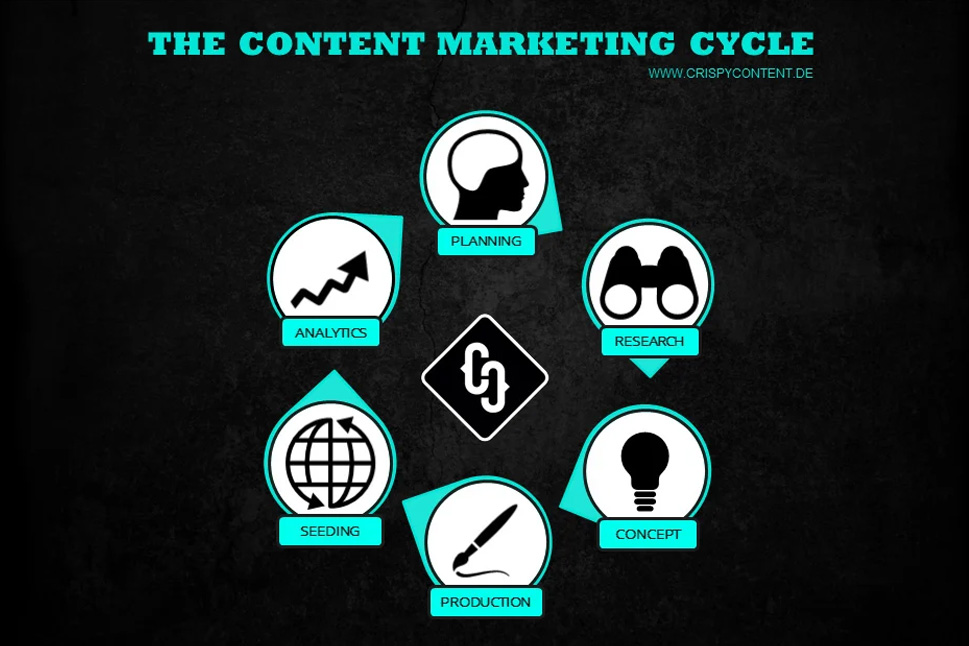
Fundamentals of Modern AI Content Tools
AI content tools refer to software that uses machine learning to create, adapt, or analyze content. For marketing leaders, it is crucial to clearly categorize these tools to build a robust tech stack aligned with their content and brand strategy.
Key Categories in the AI Content Ecosystem
For a structured selection, it is useful to classify tools by their core function. This creates a transparent overview of which building blocks are missing in your own setup and which ones overlap. Typical categories include generative tools for text, image, audio, and video, as well as specialized solutions for research, analysis, or automation. The key is not to view these components in isolation, but as a connected architecture that supports the company’s content strategy, processes, and data landscape.
Generative Language Models for Text
Large language models such as OpenAI’s GPT or Anthropic’s Claude are central to many AI content workflows. They support the creation of landing pages, blog articles, social media posts, email sequences, whitepapers, and scripts. Agencies should focus on two key aspects: clearly defined use cases with quality criteria, and precise prompts with internal guidelines to ensure outputs are accurate, brand-compliant, and legally sound. In practice, hybrid workflows are effective: AI generates drafts or variants, while editors and subject matter experts refine tone, structure, and arguments.
Image Generation with Visual AI
Image models like DALL·E or Midjourney enable rapid creation of visual drafts, scenes, icons, or mockups. For B2B-focused agencies, key applications include quick visualizations for concepts and presentations, and support for recurring visuals in content series. Integration with corporate design guidelines is critical: colors, imagery, perspectives, and styles must be consistently defined and embedded in prompt libraries to ensure AI-generated visuals reinforce the brand image.
Scaling Audio and Video with AI
AI-powered video and audio tools generate or edit clips, voice-overs, subtitles, or short-form content for social media. For global brands, they offer additional value in localization, such as voice cloning or automated multi-language subtitling. To maximize productivity, agencies need clear standards for format lengths, story structures, speaker profiles, and quality checks, including pronunciation of product names and legal claims.
Intelligently Supporting Research and Analysis
In addition to content generation, AI-based analytics tools are playing an increasingly important role. They support the evaluation of search queries, customer insights, competitor content, and performance data. The combined use is particularly effective: AI-driven keyword or topic cluster analyses provide the foundation for content strategies, while generative models develop outlines and draft texts from these insights. The better agencies structure data sources, tracking, and reporting, the more precise AI-supported decisions can be made.
Practical Applications in Agency Business
AI content tools deliver value when applied to clearly defined use cases throughout the content lifecycle, from ideation to performance analysis. Most marketing organizations encounter recurring patterns that can be systematized.
Structured Content Ideation
AI excels at opening up idea spaces and bringing structure to early-stage brainstorming. Typical tasks include topic clustering, deriving formats from existing campaigns, or developing content series along the customer journey. Agencies use AI to quickly generate hypotheses and prioritize them with market and customer data, resulting in better briefs and clearer content roadmaps—especially valuable when budgets and resources are tight.
Drafting and Structuring Content
AI tools assist in creating outlines and drafts. An effective approach defines structure, target audience, tone, and key messages before generating text. Agencies can test different outline variants, accelerate long-form content development, and provide stakeholders with early decision points, reducing revision cycles and increasing process transparency.
AI-Assisted Search Engine Optimization
AI can accelerate SEO tasks but does not replace strategy. Advanced tools support keyword research, snippet drafts, internal linking ideas, and optimization of headlines and meta data. In professional settings, AI is used to systematically identify content gaps, align content with search intent, and cover semantic fields. Final evaluation remains with SEO and content experts, who consider search volume, competition, and business objectives.
Efficient Multilingual Content and Market Coverage
Translation and localization processes benefit greatly from AI when properly managed. Modern models provide rapid first drafts in multiple languages. Agencies typically use a multi-step process: automated pre-translation, editing by native speakers, and final approval by brand or legal stakeholders. This enables faster rollout of international campaigns, microsites, or product pages without losing nuance or technical accuracy.
Data-Driven Insights for Better Decisions
AI tools help distill large data sets and reveal patterns that manual analysis might miss. In marketing, this includes evaluating content performance, engagement signals, customer journey data, or market trends. Agencies leverage these insights to optimize content portfolios, allocate budgets more effectively, and build compelling business cases for new initiatives. The greatest value arises when data interpretation, creativity, and industry expertise converge.
Ensuring Long-Term Content Quality
AI generates content quickly, but speed does not replace editorial responsibility. To maintain consistent, accurate, and legally compliant brand communication, agencies need robust quality assurance mechanisms to systematically review and refine AI outputs.
Controlled Human-AI Collaboration
“Human-in-the-loop” means experts remain involved at all critical stages. AI provides suggestions; humans make decisions. Agencies define clear review steps for each content type: subject matter approval, legal review, brand check, and editorial oversight. This approach delivers efficiency gains without compromising quality, while each project yields new insights for improved prompts and workflows.
Reliable Fact-Checking and Verification
Generative models can produce convincing but inaccurate or outdated information. Agencies require established processes for research, source verification, and currency checks. Especially in regulated industries or technical fields, thorough verification is essential. A practical solution is to base AI outputs primarily on vetted internal sources and have external information validated by experts or specialized research.
Consistent Tone and Brand Style
Brands thrive on recognizability in language, visuals, and storytelling. AI-generated content must seamlessly integrate into existing brand guidelines. This includes defined language styles, preferred lines of argumentation, levels of clarity, and typical wording lists. Agencies translate these requirements into concrete prompt rules, sample texts, and internal checklists. The result is a repeatable process that reliably keeps AI outputs on brand—regardless of which team member is working with it at any given time.
Avoiding Plagiarism and Legal Risks
While generative models create new combinations, there is still a risk of similarity to existing works. Professional workflows include plagiarism checks and editorial rewrites before publication. Internal standards also matter: defining acceptable sources, citation practices, and appropriate text length and detail. Clear governance prevents avoidable copyright risks.
Seamless Integration into Existing Workflows
AI delivers value as an integrated part of editorial and campaign processes, not as a standalone solution. For marketing leaders, the key is to extend existing systems, roles, and processes without overwhelming the organization.
Embedding AI in Editorial Workflows
Professional implementation starts by defining process steps where AI adds value: topic planning, briefing, outline development, drafting, optimization, localization, and performance review. For each step, specify the tool, required inputs, and expected quality. This creates a clear, repeatable editorial process that combines predictability and speed.
Effective Interfaces with Existing Systems
Marketing teams often use a diverse tool landscape—from CMS and marketing automation to project management and DAM systems. AI should integrate seamlessly, not create new silos. Practical solutions include CMS integrations, browser extensions for research, or plugin ecosystems that embed AI functions directly into workflows. Fewer system breaks mean higher team adoption and measurable efficiency gains.
Intelligent Automation of Routine Processes
AI is particularly valuable for recurring, well-structured tasks: product description variations, social post adaptations, basic reporting, UTM generation, or initial campaign analysis. AI handles the groundwork, while experts review and finalize. This relieves teams of repetitive tasks, freeing up capacity for strategic and creative work that enhances perceived agency value.
Organizing Collaboration Between Experts and AI
Human-AI collaboration requires clear roles, responsibilities, and communication rules. In agency setups, a clear division works well: AI assists with research, structure, drafts, and variants; experts handle evaluation, prioritization, refinement, and alignment with business goals. Transparent processes reduce team uncertainty and make it easier to justify results to stakeholders.
Targeted Resource Optimization
When used correctly, AI enables better utilization of budgets and personnel. Time savings occur in concept development, content production, localization, and report preparation. Freed-up resources can be redirected to strategic initiatives such as brand positioning, customer experience, or data-driven campaigns—areas with the highest business impact.
Responsible Use of Artificial Intelligence
As AI adoption in marketing grows, so do requirements for ethics, transparency, and compliance. International organizations with complex stakeholder structures expect agencies to have clear positions and robust policies.
Transparency in Automated Content Creation
Transparency is key to building trust. Professional agencies document where AI is used in projects and inform clients about processes, tools, and control mechanisms. Clearly defined usage parameters make it easier to meet compliance requirements, ensure auditability, and adhere to client policies.
Clear Labeling and Traceability
Depending on industry, platform, and jurisdiction, labeling AI-assisted content may be required or advisable. Regardless of legal mandates, internal logging is recommended: tracking which content was AI-generated or edited, version histories, and final approvers. This documentation enhances traceability and simplifies future audits or updates.
Strict Data Protection and Rights Management
When using AI tools, protecting client data, user information, and confidential project details is paramount. Agencies must ensure sensitive data is not inadvertently shared with external systems and review vendor contracts regarding storage, training, and data sharing. Copyright issues, especially for generated images or audio, must also be legally assessed. Clear agreements and technical safeguards are essential.
Minimizing Algorithmic Bias
AI systems can replicate or amplify biases present in training data. In brand communications, this can lead to problematic representations or discriminatory language. Agencies need sensitivity and clear guidelines for reviewing, adapting, or rejecting content. Diversity, inclusion, and brand values must be consciously integrated into the development and evaluation of AI-generated content.

Economic Evaluation of AI Investments
For Heads of Marketing, Marketing Directors, or CMOs, the key question is: Does investing in AI content tools pay off? Structured cost-benefit analyses, considering both direct and indirect effects, provide the answer.
Assessing Licensing Models and Tool Landscape
AI tools range from free basic versions to usage-based pricing and enterprise licenses with SLAs, data protection, and integration options. Professional selection considers not only license costs but also implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance. A focused core landscape of well-integrated tools is preferable to a multitude of isolated solutions.
Quantifying Time Savings and Process Gains
The most visible benefits are reduced turnaround times for recurring tasks. To measure these, agencies track average creation times before and after AI adoption, number of feedback cycles, or campaign time-to-market. These metrics provide a solid basis for decisions at the executive and finance levels.
Measurable Content Quality Improvements
Quality can be assessed objectively: longer dwell times, higher conversion rates, improved SEO rankings, lower bounce rates, or a more consistent brand image across touchpoints. AI helps tailor content to user needs, test hypotheses faster, and efficiently apply learnings to new content.
Calculating Return on Investment
A robust ROI analysis combines tool and implementation costs with quantified time savings and performance improvements. Qualitative effects—such as improved planning, reduced reliance on freelancers, or higher internal stakeholder satisfaction—should also be considered. A structured model enables informed decisions on AI investment priorities.
Build or Buy: Making the Right Choice
Larger organizations must decide whether to develop proprietary AI solutions or leverage existing platforms. Criteria include data protection, integration needs, innovation speed, and internal expertise. Often, a hybrid approach is optimal: strategic core functions are integrated in-house or run on proprietary data, while specialized features are sourced externally.
Empowering Teams for AI Adoption
Technology alone is not enough. The key is how well teams understand, operate, and integrate AI into daily work. For marketing leaders, enablement is crucial to unlocking potential and mitigating risks.
Building Prompt Engineering Skills
The quality of AI outputs depends largely on input quality. Professionally crafted prompts clearly define objectives, roles, target audiences, tone, structure, and constraints. Agencies invest in training teams to work systematically with examples, iterations, and feedback, establishing internal best practices that accelerate workflows and enhance consistency.
Standardizing Proven Approaches
What works well should be repeatable. Successful prompts, process designs, and quality assurance routines are documented and shared within the team. This turns individual experiments into standards for entire content pipelines, campaigns, or markets, facilitating scalability and reliability across locations, languages, and business units.
Targeted Training for Specialized Tools
Depending on the tool landscape, teams require specific expertise—for example in image models, video platforms, analytics tools, or integrations with CMS and marketing automation systems. Tool-specific workshops deepen the understanding of capabilities, limitations, and common pitfalls. What matters most is a hands-on focus: realistic use cases, concrete examples from the brand’s or product’s own context, and templates that can be used immediately.
Embedding a Culture of Continuous Learning
AI technology evolves rapidly. Instead of one-off training, teams need a culture of ongoing learning: internal showcases, brown-bag sessions, documentation of new insights, and regular workflow reviews. This ensures organizational agility as tools, markets, or legal frameworks change.
Proactively Managing Change
AI adoption changes roles and workflows. To reduce uncertainty, leaders should communicate early about which tasks will be automated, expanded, or redefined. Clarity on goals, opportunities, and limitations supports team buy-in. Addressing concerns about job security or control, while highlighting new development and career paths, is equally important.
Outlook for Agencies and Marketing Organizations
AI will have a lasting impact on marketing and communications. Agencies and companies that experiment systematically, establish clear guidelines, and empower their teams can leverage this development—strategically, creatively, and economically.
Strategically Harnessing New Technological Capabilities
With each generation, AI models become more precise, multimodal, and integrable. For marketing leaders, now is the time to position their organizations for scalability and flexibility. A solid foundation—data, processes, governance—enables rapid adoption of new features without starting from scratch each time.
Recognizing Potential and Respecting Limitations
AI excels at pattern recognition, speed, and scale, but is limited in contextual depth, genuine empathy, and strategic judgment. Successful agencies deploy AI where it adds value and rely on experienced professionals for critical, reputation-sensitive decisions. This balance avoids both naive tech optimism and unnecessary roadblocks.
Shifting Roles and Collaboration Models
Marketing team roles are evolving: less manual production, more orchestration, evaluation, and management. Content and campaign leads become conductors of an expanded ecosystem of people, tools, and data. Agencies that address this shift early can act as partners in organizational development, skill-building, and change management.
Developing New Services and Business Models
AI creates opportunities for new offerings: AI governance consulting, prompt library development, “human-in-the-loop” content factories, data-driven always-on optimization, or AI-powered personalization. For marketing leaders, this means more options to align budgets with measurable outcomes and enhance collaboration quality with external partners.
Preparing Organizations for Change
Viewing AI as an infrastructural shift, not a short-term trend, requires multi-year planning: tool and data architecture roadmaps, team skill profiles, governance models, and clear visions for marketing’s contribution to business success. With this foundation, AI can make communication and content strategies not just more efficient, but fundamentally better.


















.png)










.jpg)
-1.jpg)

-1.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)













.jpg)






.jpg)





























.jpg)